Mahlum has reached an important milestone in our continued evolution by expanding our leadership: Abby Dacey and PJ Bauser have both been elevated to the role of Partner and join the ownership group in guiding the strategic direction of the firm and upholding our core values and vision.
Abby and PJ have each played a vital role in shaping Mahlum’s future and strengthening our presence across markets, within our industry, and within our communities. We are confident they will continue to contribute meaningfully to the work that defines us.
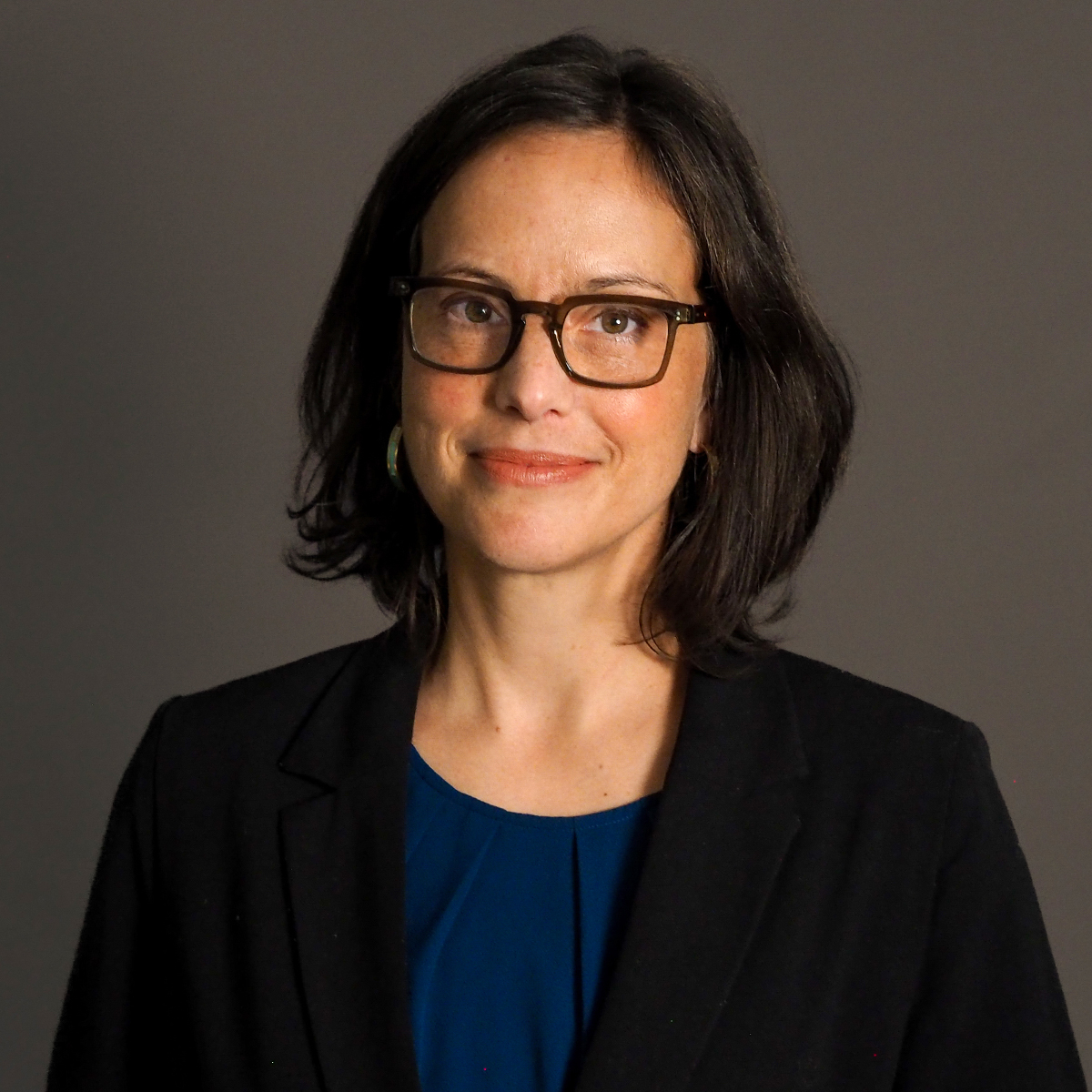

ABBY DACEY AIA LEED AP, PARTNER
Since joining Mahlum in 2016, Abby Dacey has expanded Mahlum’s PK-12 work based in Oregon and Southwest Washington. Drawing on her 24 years of experience in early learning and PK-12 educational facilities, Abby’s passion for design thinking and community empowerment are making a lasting impact on our region and the architectural profession. While Abby will continue her leadership role in the firm’s PK-12 educational work, she has also expanded her influence across Mahlum’s broader community engagement efforts.
With a clear passion for meaningful impact, Abby leads Mahlum’s Commitment to Community program, which guides the firm’s pro bono design work in service of the communities we support. She also oversees Mahlum’s Charitable Giving program, directing resources to mission-aligned, community-based nonprofits and forging partnerships with organizations that share the firm’s values. Within and beyond her work at Mahlum, Abby is a strong advocate for early childhood education—working to reduce barriers to opening preschools by promoting systems change and helping providers navigate complex regulatory processes.
Abby is also deeply committed to inspiring the next generation of architects. She helped establish Mahlum’s Internship Program, which brings students into our offices each summer, and continues to mentor emerging talent through partnerships with local universities. Her passion for design education extends into the community, where she serves on the board of the Architecture Foundation of Oregon (AFO), connecting local middle and high school students with opportunities in the AEC industry.
“Abby brings a deep commitment to inclusivity and equity, grounded in her belief that every individual is an expert in their own lived experience. She is a passionate advocate for building a profession that truly reflects the communities we serve. Her leadership as a Partner continues to guide and strengthen our firm toward a more equitable future.”
Corrie Rosen, Partner
Mahlum Architects
Since joining Mahlum, Abby has led several impactful projects that reflect her commitment to community-centered design. Notable work includes leadership in prioritizing the community’s input to enhance equity, resiliency, and sustainability at the new Lakeridge Middle School in Lake Oswego, Oregon, which received a 2024 AIA Committee on Architecture for Education (CAE) Facility Design Award. Recently, she guided the design of a new Cornelius Elementary School in Forest Grove, Oregon, that reflects the bilingual community it serves. Abby is also currently leading the modernization of Cleveland High School in Portland, Oregon, incorporating the voices of hundreds of students, staff, families, and neighbors to develop a dynamic campus.
PJ BAUSER AIA ACHA LEED AP, PARTNER
PJ Bauser holds 20 years of experience in healthcare design. Since joining Mahlum in 2007, PJ has played a key role in advancing the firm’s award-winning healthcare practice, applying thoughtful and innovative design strategies that reflect the unique character and culture of each place. As a newly named Partner, PJ will continue to lead Mahlum’s healthcare work while also deepening his focus on helping shape and support the well-being of the employee experience.
PJ is not only a leader in healthcare design but also a committed mentor, known for his generosity in sharing knowledge and fostering the growth of his team. In 2014, he led a strategic re-evaluation of Mahlum’s healthcare practice, shifting the focus from large institutions and onto community-based organizations that provide personalized, meaningful care.
With a focus on fostering a supportive and engaging workplace where people can thrive, grow, and build meaningful careers, PJ is leading efforts to further enrich the employee experience at Mahlum. He fosters collaborative teams that prioritize deep listening—ensuring every voice is heard and valued.
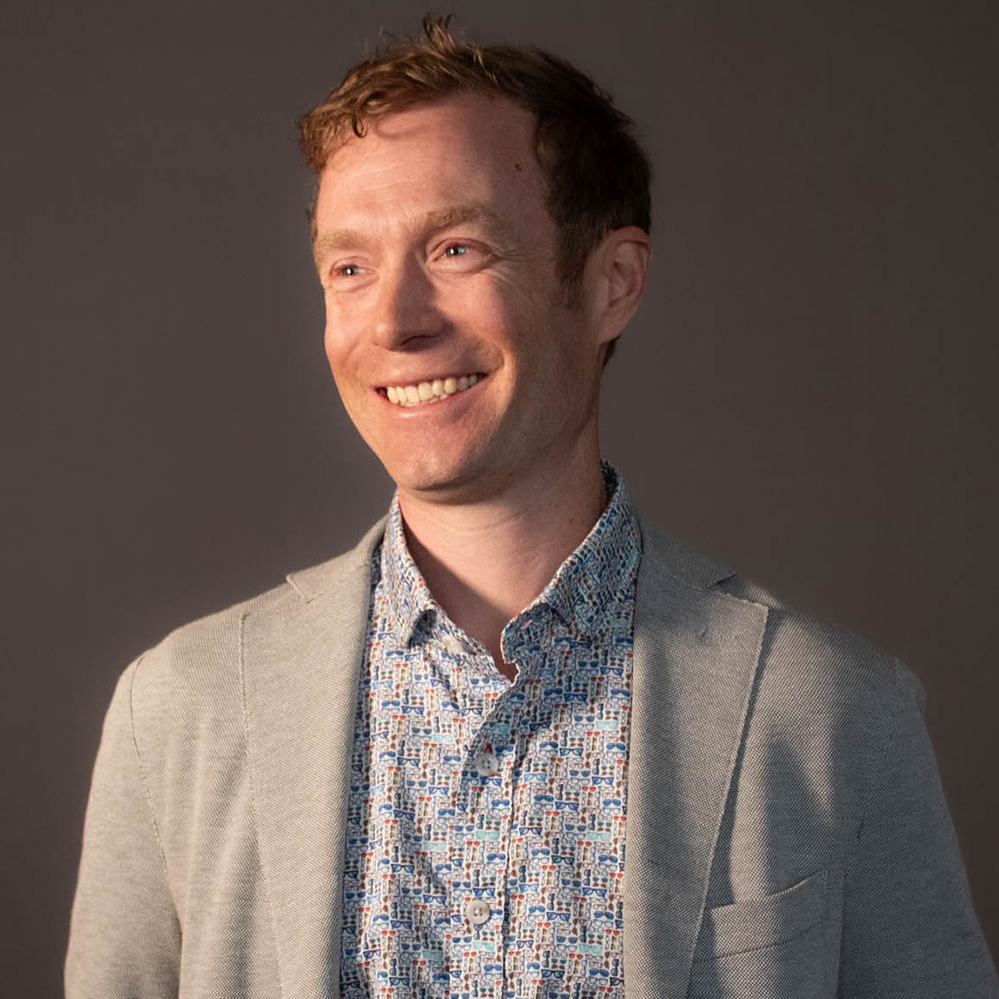

“Under PJ’s thoughtful leadership, Mahlum’s healthcare work has pivoted to prioritizing community-centered design with a focus on improving local health outcomes—especially in rural and underserved areas.”
Mark Cork, Partner
Mahlum Architects
His commitment to equity and inclusion is reflected in his leadership of the firm’s partnership with Future Workplace Design (FWD), which includes staff training, employee listening sessions, and identifying strategies to better support employees. Through these initiatives—and projects like the pro bono Heron’s Nest outdoor cooking pavilion with Sawhorse Revolution on land rematriated to the Duwamish Tribe—PJ is helping shape a culture where multiple perspectives and open dialogue drive lasting, positive change.
PJ has been a key force behind some of Mahlum’s most innovative healthcare projects. Notable work includes the 2021 AIA Committee on the Environment (COTE) Top Ten Award winning Rainier Beach Clinic for Northwest Kidney Centers in Seattle, Washington which places patients at the center of the design process; Snoqualmie Valley Health’s new Medical Office Building which transforms the outpatient experience into a welcoming, community-oriented destination. PJ’s passion to create healthful, supportive environments for providers and caregivers continues to drive the evolution of Mahlum’s healthcare practice.